Q9. A square lawn has a 2 m wide path surrounding it. If the area of the path is 136 sq metre, find the area of the lawn.
Sol.

According to diagram, PQRS is the square lawn and ABCD is outer boundary i.e lawn with path.
Let’s assume that side of the lawn be x m.
\begin{array}{l} \text {Area of the square lawn PQRS}=x^{2} \\ \text {Given that width of path around the lawn is 2 m wide.} \\ \therefore \text {Length of side of outer boundary}=(x+2+2)=(x+4) \text { m} \\ \text {Area of ABCD } =(x+4)^{2} \\ =(x^{2}+8x+16) \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Given area of the path} = 136 \text { m}^{2} \\ \text {Area of the path}= \text {Area of ABCD} – \text {Area of the square lawn PQRS } \\ \Rightarrow \quad 136=(x^{2}+8 x+16) – x^{2} \\ \Rightarrow \quad 136=8 x+16 \\ \Rightarrow \quad 8 x = 136-16 \\ \Rightarrow \quad x =\frac {120}{8} =15 \\ \text {Hence, side of the square lawn is 15 m.} \\ \text {And so, Area of the lawn }=(15)^{2}=225 \text { m}^{2} \end{array}Q10. A poster of size 10 cm by 8 cm is pasted on a sheet of cardboard such that there is a margin of width 1.75 cm along each side of the poster. Find
(i) the total area of the margin
(ii) the cost of the cardboard used at the rate of Rs. 0.60 per sq cm.
Sol.

Given length of poster = 10 cm.
And breadth of poster = 8 cm.
\begin{array}{l} \text {Area of the poster }= \text {Length} \times \text {Breadth} =10 \times 8 =80 \text { cm}^{2} \\\text {Length of the cardboard with margin} =10 +1.75 +1.75 =13.5 \text { cm} \\\text {Breadth of the cardboard with margin} =8 +1.75 +1.75 =11.5 \text { cm} \\ \text {Area of the cardboard }= \text {Length} \times \text {Breadth} =13.5 \times 11.5 \\ =155.25 \text { cm}^{2} \\ \\\text {(i) Area of the margin } = \text {Area of cardboard with margin} – \text {Area of the poster} \\ =155.25 -80 =75.25 \text { cm}^{2} \\ \\\text {(ii) Cost of the cardboard }= \text {Area of cardboard} \times \text {Rate of the cardboard per sq. cm} \\ =155.25 \times 0.60 =\text {Rs. } 93.15 \end{array}Q11. A rectangular field is 50 m by 40 m. It has two roads through its centre, running parallel to its sides. The width of the longer and shorter roads are 1.8 m and 2.5 m respectively. Find the area of the roads and the area of the remaining portion of the field.
Sol.

\begin{array}{l}\text {Length of the rectangular field }=50 \text { m} \\ \text {Breadth of the rectangular field }=40 \text { m} \\\text {Area of the rectangular field }=50 \text { m} \times 40 \text { m}=2000 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the road EFGH where widht is 1.8 m}=50 \text { m} \times 1.8 \text { m}=90 \text { m}^{2} \\ \text {Area of the road PQRS where widht is 2.5 m}=40 \text { m} \times 2.5 \text { m}=100 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of IJKL}=2.5 \text { m} \times 1.8 \text { m}=4.5\text { m}^{2} \\ \text {Clearly, area of IJKL is common in two roads.} \\ \text {Hence, combined area covered by two roads } \\ = \text {Area of EFGH} + \text {Area of PQRS} – \text {Area of IJKL} \\ =90 + 100 -4.5 =185.5 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the field without roads} \\ = \text {Area of the rectangular field ABCD} – \text {Combined area of the roads} \\ =2000-185.5 \text{ m}^{2} \\ =1814.5 \text{ m}^{2} \\ \end{array}Q12. There is a rectangular field of size 94 m x 32 m. Three roads each of 2 m width pass through the field such that two roads are parallel to the breadth of the field and the third is parallel to the length. Calculate:
(i) area of the field covered by the three roads
(ii) area of the field not covered by the roads.
Sol.

Length of the rectangular field = 94 m.
Breadth of the rectangular field = 32 m.
\begin{array}{l} \text {Area of the rectangular field }=94 \text { m} \times 32 \text { m}=3008 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the road EFGH where widht is 2 m}=94 \text { m} \times 2 \text { m}=188 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the road PQRS}=32 \text { m} \times 2 \text { m}=64 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the road MNOP}=32 \text { m} \times 2 \text { m}=64 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of IJKL} = \text {Area of WXYZ} =2 \text { m} \times 2 \text { m}=4 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Clearly, area of IJKL and WXYZ are common in two roads.} \\ \text {Hence, combined area covered by 3 roads } \\ = \text {Area of EFGH} + \text {Area of PQRS} + \text {Area of MNOP} – \text {Area of IJKL} – \text {Area of WXYZ} \\ =188 + 64 + 64 -4 – 4 =308 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the field without roads} \\ = \text {Area of the rectangular field ABCD} – \text {Combined area of the roads} \\ =3008 – 308 \text{ m}^{2} \\ =2700 \text{ m}^{2} \\ \end{array}Q13. A school has a hall which is 22 m long and 15.5 m broad. A carpet is laid inside the hall leaving all around a margin of 75 cm from the walls. Find the area of the carpet and the area of the strip left uncoverd. If the width of the carpet is 82 cm, find the cost at the rate of Rs. 18 per metre.
Sol.

Given that length of hall AB = 22 m.
And breadth of hall BC = 15.5 m.
\begin{array}{l}\text {Area of the hall ABCD } =22 \times 15.5 =341 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Length of the carpet PQ } =22 – 0.75 0.75 \quad [\because 75 \text { cm} = \frac {75}{100} \text { m} = 0.75 \text { m}] \\=20.5 \text { m} \\\text {Breadth of the carpet QR }=15.5 – 0.75 +0.75 =14 \text { m} \\\text {Area of the carpet PQRS } =20.5 \times 14 =287 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the strip }= \text {Area of the hall ABCD } – \text {Area of the carpet PQRS} \\ =341 -287 =54 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {New width of carpet } = 82 \text { cm} = 0.82 \text { m} \\ \text {Lets assume length of carpet be x m} \\ \text {Area of carpet } = \text {Lenght} \times \text {Breadth} \\ \Rightarrow \quad 287 = 0.82 x \\ \Rightarrow \quad x = \frac {287}{0.82} \\ \Rightarrow \quad x = 350 \text { m} \\ \text {Given cost of 1 metre carpet} = \text {Rs. } 18 \\ \text {Hence, cost of the 350 m long carpet }=\text {Rs. } 18 \times 350 = \text {Rs. } 6300 \end{array}Q14. Two cross roads, each of width 5 m, run at right angles through the centre of a rectangular park of length 70 m and breadth 45 m parallel to its sides. Find the area of the roads. Also, find the cost of constructing the roads at the rate of Rs 105 per sq. metre.
Sol.

Length of the rectangular park =70 m.
Breadth of the rectangular park = 45 m.
\begin{array}{l} \text {Area of the rectangular park }=70 \text { m} \times 45 \text { m}=3150 \text { m}^{2} \\ \text {Area of the road EFGH}=70 \text { m} \times 5 \text { m}=350 \text { m}^{2} \\ \text {Area of the road PQRS}=45 \text { m} \times 5 \text { m}=225 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of IJKL}=5 \text { m} \times 5 \text { m}=25 \text { m}^{2} \\ \text {Clearly, area of IJKL is common in two roads.} \\ \text {Hence, combined area covered by two roads }= \text {Area of EFGH} + \text {Area of PQRS} – \text {Area of IJKL} =350 + 225 – 25 =550 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Given rate of constructing of the roads is Rs. 105 per sq. metre.} \\ \therefore \text {Cost of constructing of } 550 \text { m}^{2} \text { area of the roads }= \text {Rs. } 105 \times 550 \\ = \text {Rs. } 57750 \end{array}Q15. The length and breadth of a rectangular park are in the ratio 5 : 2. A 2.5 m wide path running all around the outside the park has an area 305 sq m. Find the dimensions of the park.
Sol.

Lets assume that the length of the park be 5x metre.
And breadth be 2 x metre.
\begin{array}{l} \therefore \text {Area of the rectangular park }=5x \times 2x =10 x^{2} \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Width of the path } =2.5 \text { m} \\\text {Outer length AB}= 5x+ 2.5 +2.5 =(5 x+5) \text { m} \\ \text {Outer breadth BC }=2x + 2.5 + 2.5 =(2 x+5) \text { m} \\ \text {Area of ABCD } =(5 x+5)(2 x+5) \\ =(10 x^{2}+35 x+25) \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Given that area of the park is } 305 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the path }=\text {Area of ABCD } – \text {Area of rectangular park } \\ \Rightarrow \quad 305 =(10 x^{2}+35x+25)-10 x^{2} \text { m}^{2} \\ \Rightarrow \quad 305=35x+25 \\ \Rightarrow \quad 35x = 305 – 25 \\ \Rightarrow \quad x = \frac {280}{35} \\ \Rightarrow \quad x = 8 \\ \therefore \text {Length of the park } =5 x =5 \times 8=40 \text { m} \\ \text {Breadth of the park }=2 x =2 \times 8=16 \text { m} \\ \end{array}Q16 . A square lawn is surrounded by a path 2.5 m wide. If the area of the path is 165 sq m, find the area of the lawn.
Sol.

Lets assume that the side of lawn be x m.
Given that width of the path = 2.5 m.
Side of the lawn including the path = x + 2.5 + 2.5 = (x+5) m.
\begin{array}{l} \text {Give that area of the path is } 165 \text { m}^{2} \\ \therefore \text {Area of lawn }=\text {Area of the lawn including the path}- \text {Area of the path} \\ \Rightarrow \quad x^{2} =(x+5)^{2} -165 \\ \Rightarrow \quad x^{2}=(x^{2}+10 x+25)-165 \quad \quad [\text {Using : } (a+b)^{2} = a^{2}+ b^{2} + 2ab] \\ \Rightarrow \quad 165=10 x+25 \\ \Rightarrow \quad 165-25=10 x \\ \Rightarrow \quad x = \frac {140}{10} =14\\\text {Hence, side of the lawn is 14 metres.} \\ \therefore \text {The area of the lawn } =(14)^{2} =196 \text { m}^{2} \end{array}
Sol.
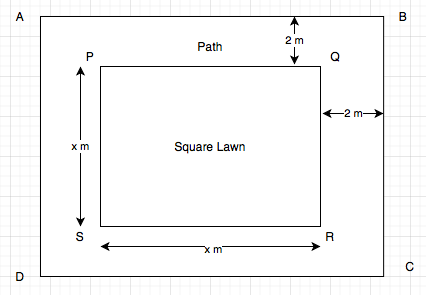
According to diagram, PQRS is the square lawn and ABCD is outer boundary i.e lawn with path.
Let’s assume that side of the lawn be x m.
\begin{array}{l} \text {Area of the square lawn PQRS}=x^{2} \\ \text {Given that width of path around the lawn is 2 m wide.} \\ \therefore \text {Length of side of outer boundary}=(x+2+2)=(x+4) \text { m} \\ \text {Area of ABCD } =(x+4)^{2} \\ =(x^{2}+8x+16) \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Given area of the path} = 136 \text { m}^{2} \\ \text {Area of the path}= \text {Area of ABCD} – \text {Area of the square lawn PQRS } \\ \Rightarrow \quad 136=(x^{2}+8 x+16) – x^{2} \\ \Rightarrow \quad 136=8 x+16 \\ \Rightarrow \quad 8 x = 136-16 \\ \Rightarrow \quad x =\frac {120}{8} =15 \\ \text {Hence, side of the square lawn is 15 m.} \\ \text {And so, Area of the lawn }=(15)^{2}=225 \text { m}^{2} \end{array}Q10. A poster of size 10 cm by 8 cm is pasted on a sheet of cardboard such that there is a margin of width 1.75 cm along each side of the poster. Find
(i) the total area of the margin
(ii) the cost of the cardboard used at the rate of Rs. 0.60 per sq cm.
Sol.
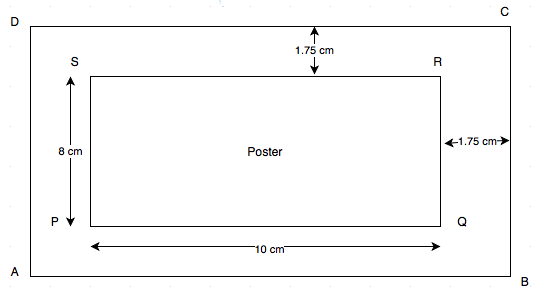
Given length of poster = 10 cm.
And breadth of poster = 8 cm.
\begin{array}{l} \text {Area of the poster }= \text {Length} \times \text {Breadth} =10 \times 8 =80 \text { cm}^{2} \\\text {Length of the cardboard with margin} =10 +1.75 +1.75 =13.5 \text { cm} \\\text {Breadth of the cardboard with margin} =8 +1.75 +1.75 =11.5 \text { cm} \\ \text {Area of the cardboard }= \text {Length} \times \text {Breadth} =13.5 \times 11.5 \\ =155.25 \text { cm}^{2} \\ \\\text {(i) Area of the margin } = \text {Area of cardboard with margin} – \text {Area of the poster} \\ =155.25 -80 =75.25 \text { cm}^{2} \\ \\\text {(ii) Cost of the cardboard }= \text {Area of cardboard} \times \text {Rate of the cardboard per sq. cm} \\ =155.25 \times 0.60 =\text {Rs. } 93.15 \end{array}Q11. A rectangular field is 50 m by 40 m. It has two roads through its centre, running parallel to its sides. The width of the longer and shorter roads are 1.8 m and 2.5 m respectively. Find the area of the roads and the area of the remaining portion of the field.
Sol.
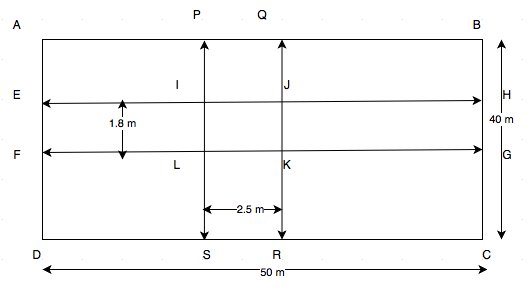
\begin{array}{l}\text {Length of the rectangular field }=50 \text { m} \\ \text {Breadth of the rectangular field }=40 \text { m} \\\text {Area of the rectangular field }=50 \text { m} \times 40 \text { m}=2000 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the road EFGH where widht is 1.8 m}=50 \text { m} \times 1.8 \text { m}=90 \text { m}^{2} \\ \text {Area of the road PQRS where widht is 2.5 m}=40 \text { m} \times 2.5 \text { m}=100 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of IJKL}=2.5 \text { m} \times 1.8 \text { m}=4.5\text { m}^{2} \\ \text {Clearly, area of IJKL is common in two roads.} \\ \text {Hence, combined area covered by two roads } \\ = \text {Area of EFGH} + \text {Area of PQRS} – \text {Area of IJKL} \\ =90 + 100 -4.5 =185.5 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the field without roads} \\ = \text {Area of the rectangular field ABCD} – \text {Combined area of the roads} \\ =2000-185.5 \text{ m}^{2} \\ =1814.5 \text{ m}^{2} \\ \end{array}Q12. There is a rectangular field of size 94 m x 32 m. Three roads each of 2 m width pass through the field such that two roads are parallel to the breadth of the field and the third is parallel to the length. Calculate:
(i) area of the field covered by the three roads
(ii) area of the field not covered by the roads.
Sol.
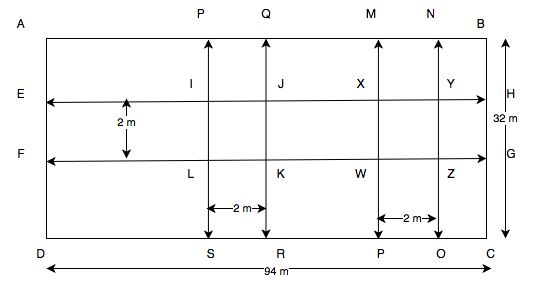
Length of the rectangular field = 94 m.
Breadth of the rectangular field = 32 m.
\begin{array}{l} \text {Area of the rectangular field }=94 \text { m} \times 32 \text { m}=3008 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the road EFGH where widht is 2 m}=94 \text { m} \times 2 \text { m}=188 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the road PQRS}=32 \text { m} \times 2 \text { m}=64 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the road MNOP}=32 \text { m} \times 2 \text { m}=64 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of IJKL} = \text {Area of WXYZ} =2 \text { m} \times 2 \text { m}=4 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Clearly, area of IJKL and WXYZ are common in two roads.} \\ \text {Hence, combined area covered by 3 roads } \\ = \text {Area of EFGH} + \text {Area of PQRS} + \text {Area of MNOP} – \text {Area of IJKL} – \text {Area of WXYZ} \\ =188 + 64 + 64 -4 – 4 =308 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the field without roads} \\ = \text {Area of the rectangular field ABCD} – \text {Combined area of the roads} \\ =3008 – 308 \text{ m}^{2} \\ =2700 \text{ m}^{2} \\ \end{array}Q13. A school has a hall which is 22 m long and 15.5 m broad. A carpet is laid inside the hall leaving all around a margin of 75 cm from the walls. Find the area of the carpet and the area of the strip left uncoverd. If the width of the carpet is 82 cm, find the cost at the rate of Rs. 18 per metre.
Sol.

Given that length of hall AB = 22 m.
And breadth of hall BC = 15.5 m.
\begin{array}{l}\text {Area of the hall ABCD } =22 \times 15.5 =341 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Length of the carpet PQ } =22 – 0.75 0.75 \quad [\because 75 \text { cm} = \frac {75}{100} \text { m} = 0.75 \text { m}] \\=20.5 \text { m} \\\text {Breadth of the carpet QR }=15.5 – 0.75 +0.75 =14 \text { m} \\\text {Area of the carpet PQRS } =20.5 \times 14 =287 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the strip }= \text {Area of the hall ABCD } – \text {Area of the carpet PQRS} \\ =341 -287 =54 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {New width of carpet } = 82 \text { cm} = 0.82 \text { m} \\ \text {Lets assume length of carpet be x m} \\ \text {Area of carpet } = \text {Lenght} \times \text {Breadth} \\ \Rightarrow \quad 287 = 0.82 x \\ \Rightarrow \quad x = \frac {287}{0.82} \\ \Rightarrow \quad x = 350 \text { m} \\ \text {Given cost of 1 metre carpet} = \text {Rs. } 18 \\ \text {Hence, cost of the 350 m long carpet }=\text {Rs. } 18 \times 350 = \text {Rs. } 6300 \end{array}Q14. Two cross roads, each of width 5 m, run at right angles through the centre of a rectangular park of length 70 m and breadth 45 m parallel to its sides. Find the area of the roads. Also, find the cost of constructing the roads at the rate of Rs 105 per sq. metre.
Sol.
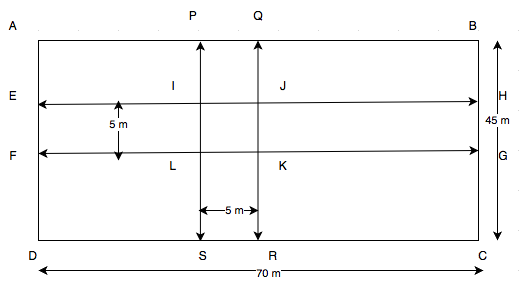
Length of the rectangular park =70 m.
Breadth of the rectangular park = 45 m.
\begin{array}{l} \text {Area of the rectangular park }=70 \text { m} \times 45 \text { m}=3150 \text { m}^{2} \\ \text {Area of the road EFGH}=70 \text { m} \times 5 \text { m}=350 \text { m}^{2} \\ \text {Area of the road PQRS}=45 \text { m} \times 5 \text { m}=225 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of IJKL}=5 \text { m} \times 5 \text { m}=25 \text { m}^{2} \\ \text {Clearly, area of IJKL is common in two roads.} \\ \text {Hence, combined area covered by two roads }= \text {Area of EFGH} + \text {Area of PQRS} – \text {Area of IJKL} =350 + 225 – 25 =550 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Given rate of constructing of the roads is Rs. 105 per sq. metre.} \\ \therefore \text {Cost of constructing of } 550 \text { m}^{2} \text { area of the roads }= \text {Rs. } 105 \times 550 \\ = \text {Rs. } 57750 \end{array}Q15. The length and breadth of a rectangular park are in the ratio 5 : 2. A 2.5 m wide path running all around the outside the park has an area 305 sq m. Find the dimensions of the park.
Sol.
Lets assume that the length of the park be 5x metre.
And breadth be 2 x metre.
\begin{array}{l} \therefore \text {Area of the rectangular park }=5x \times 2x =10 x^{2} \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Width of the path } =2.5 \text { m} \\\text {Outer length AB}= 5x+ 2.5 +2.5 =(5 x+5) \text { m} \\ \text {Outer breadth BC }=2x + 2.5 + 2.5 =(2 x+5) \text { m} \\ \text {Area of ABCD } =(5 x+5)(2 x+5) \\ =(10 x^{2}+35 x+25) \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Given that area of the park is } 305 \text { m}^{2} \\\text {Area of the path }=\text {Area of ABCD } – \text {Area of rectangular park } \\ \Rightarrow \quad 305 =(10 x^{2}+35x+25)-10 x^{2} \text { m}^{2} \\ \Rightarrow \quad 305=35x+25 \\ \Rightarrow \quad 35x = 305 – 25 \\ \Rightarrow \quad x = \frac {280}{35} \\ \Rightarrow \quad x = 8 \\ \therefore \text {Length of the park } =5 x =5 \times 8=40 \text { m} \\ \text {Breadth of the park }=2 x =2 \times 8=16 \text { m} \\ \end{array}Q16 . A square lawn is surrounded by a path 2.5 m wide. If the area of the path is 165 sq m, find the area of the lawn.
Sol.

Lets assume that the side of lawn be x m.
Given that width of the path = 2.5 m.
Side of the lawn including the path = x + 2.5 + 2.5 = (x+5) m.
\begin{array}{l} \text {Give that area of the path is } 165 \text { m}^{2} \\ \therefore \text {Area of lawn }=\text {Area of the lawn including the path}- \text {Area of the path} \\ \Rightarrow \quad x^{2} =(x+5)^{2} -165 \\ \Rightarrow \quad x^{2}=(x^{2}+10 x+25)-165 \quad \quad [\text {Using : } (a+b)^{2} = a^{2}+ b^{2} + 2ab] \\ \Rightarrow \quad 165=10 x+25 \\ \Rightarrow \quad 165-25=10 x \\ \Rightarrow \quad x = \frac {140}{10} =14\\\text {Hence, side of the lawn is 14 metres.} \\ \therefore \text {The area of the lawn } =(14)^{2} =196 \text { m}^{2} \end{array}
