Q1. Find the area in square centimetres of a triangle whose base and altitude are as under:
(i) Base =18 cm, altitude =3.5 cm
(ii) Base =8 dm, altitude =15 cm
Sol. \begin{array}{l} \text {We know that the area of a triangle }=\frac{1}{2} \times \text {Base} \times \text {Height} \\ \text {(i) Given, base =18 cm and height =3.5 cm } \\ \text {Area of the triangle }=\frac{1}{2} \times 18 \times 3.5=31.5 \text { cm}^{2} \\ \\\text {(ii) Given, base =8 dm }=8 \times 10 \text { cm} \quad \quad [\because 1 \text{ dm}=10 \text{ cm}] \\ =80 \text{ cm} \\ \text {And height }=3.5 \text{ cm} \\\text {Area of the triangle }=\frac{1}{2} \times 80 \times 15 =600 \text{cm}^{2} \end{array}Q2. Find the altitude of a triangle whose area is 42 sq cm and base is 12 cm.
Sol. \begin{array}{l} \text {Given , base =12 cm and area } =42 \text { cm}^{2} \\ \text {We know that, Altitude of a triangle }=\frac{2 \times \text { Area }}{\text { Base }} \\ \therefore \text {Altitude} =\frac{2 \times 42}{12}=7 \text{ cm} \end{array}Q3. The area of a triangle is }50 \text{ cm}^{2}. \text {If the altitude is 8 cm, what is its base?
Sol. \begin{array}{l}\text {Given , altitude =8 cm and area } =50 \text { cm}^{2} \\ \text {We know that, Base of a triangle }=\frac{2 \times \text { Area }}{\text { Altitude }} \\ \therefore \text {Base} =\frac{2 \times 50}{8}=12.5 \text{ cm} \end{array}Q4. Find the area of a right angled triangle whose sides containing the right angle are of lengths 20.8 m and 14.7 m.
Sol.

Given that the lenght of sides containing right angle in triangle ABC are 20.8 m and 14.7 m respectively.
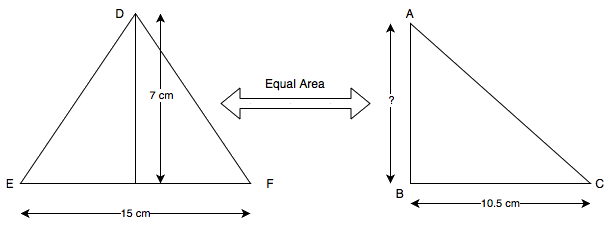
$$ \text {Lets assume that the base is 20.8 m and the height be 14.71 m in } \triangle{ABC} $$ $$ \therefore \text { Area of triangle ABC}=\frac{1}{2} \times \text {Base} \times \text {Height} $$ $$ =\frac{1}{2} \times 20.8 \times 14.7 =152.88 \text { m}^{2} $$Q5. The area of a triangle, whose base and the corresponding altitude are 15 cm and 7 cm, is equal to area of a right triangle whose one of the sides containing the right angle is 10.5 cm Find the other side of this triangle.
Sol.

For triangle DEF, we have
Base =15 cm and altitude =7 cm
\begin{array}{l} \therefore \text {Area of a triangle DEF} =\frac{1}{2} \times \text {Base} \times \text {Altitude} \\ =\frac{1}{2} \times 15 \times 7 =52.5 \text { cm}^{2} \\\text {Area of the triangle ABC } =\frac{1}{2} \times \text {Base} \times \text {Height} \\ = \frac{1}{2} \times 10.5 \times AB \\\text {Given that the area of triangle DEF and area of triangle ABC } \\ \Rightarrow \quad \frac{1}{2} \times 10.5 \times AB = 52.5 \\ \Rightarrow \quad AB = \frac {52.5 \times 2}{10.5} \\ \Rightarrow \quad AB = 10 \text { cm} \\ \end{array}Hence, other side of triangle ABC is 10 cm.
Q6. A rectangular field is 48 m long and 20 m wide. How many right triangular flower beds, whose sides containing the right angle measure 12 m and 5 m can be laid in this field?
Sol.
Given that the length of the rectangular field = 48 m.
Breadth of the rectangular field = 20 m.
\begin{array}{l} \text {Area of the rectangular field }= \text {Length} \times \text {Breadth}=48 \times 20 =960 \text { m}^{2} \\ \text {Given that right angled sides of rectangular flower bed are 12 m and 5 m respectively.} \\ \Rightarrow \text {Area of 1 right triangular flower bed }=\frac{1}{2} \times 12 \times 5 =30 \mathrm{m}^{2} \\\therefore \text {Required number of right triangular flower beds } \\ = \frac {\text {Area of rectangular field}}{\text {Area of 1 triangular flower bed}} \\ =\frac{960}{30} = 32 \\\end{array}Hence, 32 triangular flower beds can be laid in rectangular field.
Q7. In Fig., ABCD is a quadriateral in which diagonal AC= 84 cm ; DL ⊥ AC, BM ⊥ AC, DL=16.5 cm and BM= 12 cm. Find the area of quadrilateral ABCD.

Sol.
Given that AC =84 cm, DL=16.5 cm and BM =12 cm. \begin{array}{l} \text {Area of triangle ADC}=\frac{1}{2} \times AC \times DL=\frac{1}{2} \times 84 \times 16.5 =693 \text { cm}^{2} \\\text {Area of triangle ABC}=\frac{1}{2} \times AC \times BM=\frac{1}{2} \times 84 \times 12 =504 \text { cm}^{2} \\\text {Hence, Area of quadrilateral ABCD } \\ = \text {Area of triangle ADC } + \text {Area of triangle ABC} \\ =693 + 504= 1197 \text { cm}^{2} \\\end{array}Q8. Find the area of the quadrilateral ABCD given in Fig. The diagonals AC and BD measure 48 m and 32 m respectively and are perpendicular to each other.

Sol.
Given that diagonal AC=48 m and diagonal BD=32 m. $$ \text {Area of a quadrilateral ABCD } =\frac{1}{2}(\text { Product of diagonals }) $$$$ =\frac{1}{2}(48 \times 32) =768 \text { m}^{2} $$
(i) Base =18 cm, altitude =3.5 cm
(ii) Base =8 dm, altitude =15 cm
Sol. \begin{array}{l} \text {We know that the area of a triangle }=\frac{1}{2} \times \text {Base} \times \text {Height} \\ \text {(i) Given, base =18 cm and height =3.5 cm } \\ \text {Area of the triangle }=\frac{1}{2} \times 18 \times 3.5=31.5 \text { cm}^{2} \\ \\\text {(ii) Given, base =8 dm }=8 \times 10 \text { cm} \quad \quad [\because 1 \text{ dm}=10 \text{ cm}] \\ =80 \text{ cm} \\ \text {And height }=3.5 \text{ cm} \\\text {Area of the triangle }=\frac{1}{2} \times 80 \times 15 =600 \text{cm}^{2} \end{array}Q2. Find the altitude of a triangle whose area is 42 sq cm and base is 12 cm.
Sol. \begin{array}{l} \text {Given , base =12 cm and area } =42 \text { cm}^{2} \\ \text {We know that, Altitude of a triangle }=\frac{2 \times \text { Area }}{\text { Base }} \\ \therefore \text {Altitude} =\frac{2 \times 42}{12}=7 \text{ cm} \end{array}Q3. The area of a triangle is }50 \text{ cm}^{2}. \text {If the altitude is 8 cm, what is its base?
Sol. \begin{array}{l}\text {Given , altitude =8 cm and area } =50 \text { cm}^{2} \\ \text {We know that, Base of a triangle }=\frac{2 \times \text { Area }}{\text { Altitude }} \\ \therefore \text {Base} =\frac{2 \times 50}{8}=12.5 \text{ cm} \end{array}Q4. Find the area of a right angled triangle whose sides containing the right angle are of lengths 20.8 m and 14.7 m.
Sol.

Given that the lenght of sides containing right angle in triangle ABC are 20.8 m and 14.7 m respectively.
$$ \text {Lets assume that the base is 20.8 m and the height be 14.71 m in } \triangle{ABC} $$ $$ \therefore \text { Area of triangle ABC}=\frac{1}{2} \times \text {Base} \times \text {Height} $$ $$ =\frac{1}{2} \times 20.8 \times 14.7 =152.88 \text { m}^{2} $$Q5. The area of a triangle, whose base and the corresponding altitude are 15 cm and 7 cm, is equal to area of a right triangle whose one of the sides containing the right angle is 10.5 cm Find the other side of this triangle.
Sol.
For triangle DEF, we have
Base =15 cm and altitude =7 cm
\begin{array}{l} \therefore \text {Area of a triangle DEF} =\frac{1}{2} \times \text {Base} \times \text {Altitude} \\ =\frac{1}{2} \times 15 \times 7 =52.5 \text { cm}^{2} \\\text {Area of the triangle ABC } =\frac{1}{2} \times \text {Base} \times \text {Height} \\ = \frac{1}{2} \times 10.5 \times AB \\\text {Given that the area of triangle DEF and area of triangle ABC } \\ \Rightarrow \quad \frac{1}{2} \times 10.5 \times AB = 52.5 \\ \Rightarrow \quad AB = \frac {52.5 \times 2}{10.5} \\ \Rightarrow \quad AB = 10 \text { cm} \\ \end{array}Hence, other side of triangle ABC is 10 cm.
Q6. A rectangular field is 48 m long and 20 m wide. How many right triangular flower beds, whose sides containing the right angle measure 12 m and 5 m can be laid in this field?
Sol.
Given that the length of the rectangular field = 48 m.
Breadth of the rectangular field = 20 m.
\begin{array}{l} \text {Area of the rectangular field }= \text {Length} \times \text {Breadth}=48 \times 20 =960 \text { m}^{2} \\ \text {Given that right angled sides of rectangular flower bed are 12 m and 5 m respectively.} \\ \Rightarrow \text {Area of 1 right triangular flower bed }=\frac{1}{2} \times 12 \times 5 =30 \mathrm{m}^{2} \\\therefore \text {Required number of right triangular flower beds } \\ = \frac {\text {Area of rectangular field}}{\text {Area of 1 triangular flower bed}} \\ =\frac{960}{30} = 32 \\\end{array}Hence, 32 triangular flower beds can be laid in rectangular field.
Q7. In Fig., ABCD is a quadriateral in which diagonal AC= 84 cm ; DL ⊥ AC, BM ⊥ AC, DL=16.5 cm and BM= 12 cm. Find the area of quadrilateral ABCD.

Sol.
Given that AC =84 cm, DL=16.5 cm and BM =12 cm. \begin{array}{l} \text {Area of triangle ADC}=\frac{1}{2} \times AC \times DL=\frac{1}{2} \times 84 \times 16.5 =693 \text { cm}^{2} \\\text {Area of triangle ABC}=\frac{1}{2} \times AC \times BM=\frac{1}{2} \times 84 \times 12 =504 \text { cm}^{2} \\\text {Hence, Area of quadrilateral ABCD } \\ = \text {Area of triangle ADC } + \text {Area of triangle ABC} \\ =693 + 504= 1197 \text { cm}^{2} \\\end{array}Q8. Find the area of the quadrilateral ABCD given in Fig. The diagonals AC and BD measure 48 m and 32 m respectively and are perpendicular to each other.

Sol.
Given that diagonal AC=48 m and diagonal BD=32 m. $$ \text {Area of a quadrilateral ABCD } =\frac{1}{2}(\text { Product of diagonals }) $$$$ =\frac{1}{2}(48 \times 32) =768 \text { m}^{2} $$
